sigma
 Google Cloud Datastore
Google Cloud Datastore
Google Cloud Datastore is a managed non-relational (NoSQL) entity storage. Though usually used in combination with Google App Engine, thanks to the REST API and SDK support, it is well-suited for the storage component of any applicaion, serverless, cloud or on-premise.
Datastore categorizes its content (Entities) under Kinds, similar to tables in the relational space. While it is possible to map predefined data structures to kinds (esp. in case of typed languages), Datastore usually autogenerates its kind specifications based on the structure of entities that are stored under them.
Datastore supports indexing, backup/restore, transactions and other features that make it useful in writing scalable and robust applications.
Basic Concepts
Entity keys
In Datastore, an entity is identified by a key. Sigma currently supports keys composed of entity kind and name.
Properties and data types
Each entity could additionally contain one or more properties; key-value pairs where the key is a string and the value type can be either simple or composite.
Supported simple types include:
- String
-
Boolean:
trueorfalse - Double
- Integer
- Blob: a base64-encoded binary payload
-
Null: a
nullvalue -
Timestamp:
an RFC 3339 date-time with milliseconds, of the format
yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.xxxZ
Composite types:
Array types
Additionally a property could be of array type;
in this case the value would contain a values array, which can in turn contain property entries of any type.
{
values: [
{
stringValue: "str"
},
{
geoPointValue: {
latitude: 7.4639,
longitude: 80.2985
}
},
{
arrayValue: {
values: [
...
]
}
},
...
]
}
NOTE: Sigma currently does not fully support visually composing array-type Datastore entity parameters;
however you can enter the corresponding JSON array structure (value portion of the values entry)
into the operation configuration pop-up to configure the parameter:
Name = array_field_name
Type = array (selected from drop-down)
Value = [{stringValue: "str"}, {geoPointValue: {latitude: 7.4639, longitude: 80.2985}]
Transactions
Datastore updates can be carried out in transactions. The API expects you to begin a transaction and then commit it along with the necessary data manipulations, rather than invoking the manipulation operations as separate API calls between the begin and the commit.
Mutations
A commit can contain multiple
mutations (stages),
each of which can contain up to four data manipulation calls; one from each of
the four types:
insert, update, upsert (update if exists, insert if not), and delete.
For example, a transaction could first insert A and update B, then delete C and update B again, and so forth.
Datastore does impose some rules
on the operations that can be included in a single transaction.
Sigma Commit Transaction pop-up
In the Commit Transaction pop-up, you can add new mutations to your commit operation by clicking the (+) Add button near the bottom; and remove unwanted ones by clicking the (X) Remove button under each mutation.
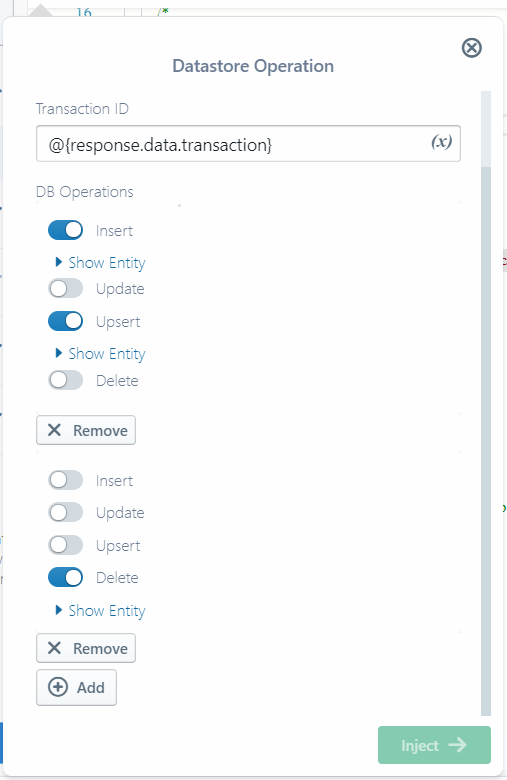
Each stage provides four toggle buttons for the four supported operations; you can enable any desired combination, and configure them using the detail pane that appears below each. Deletion needs only an entity key, while other operations need the key as well as the full set of properties of the element.
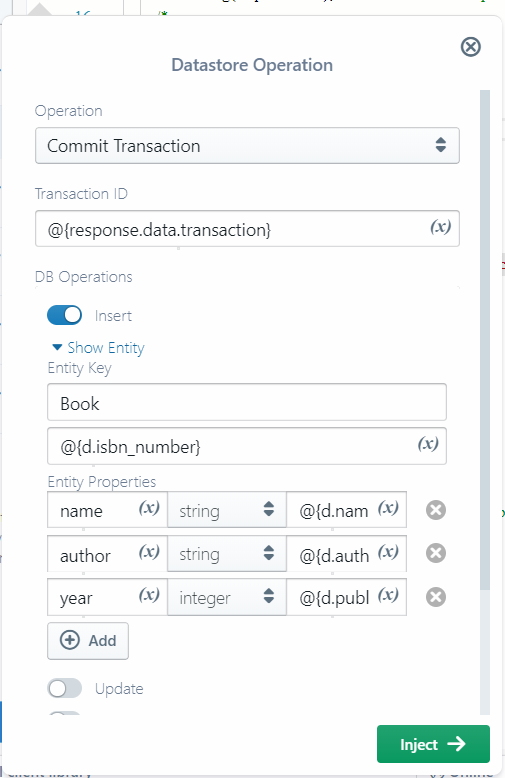
NOTE: Any properties that are present in the remote entity but not included in the update/upsert call, would be removed from the entity.
Available Datastore operations
You can invoke Datastore operations (API calls) from any platform.
Native operations
Run Query: projects.runQuery
Executes a Google Query Language (GQL) query upon the Datastore. Because GQL only supports selections, this is inherently a read-only operation.
GQL queries can be parameterized, using either or both of these parameter types:
-
named (e.g.
SELECT * FROM Foo WHERE bar = @barvalue) -
positional (e.g.
SELECT * FROM Foo WHERE baz = @1)
If your query uses such parameters you can specify them below the query via the Named Parameters and Positional Parameters fields.
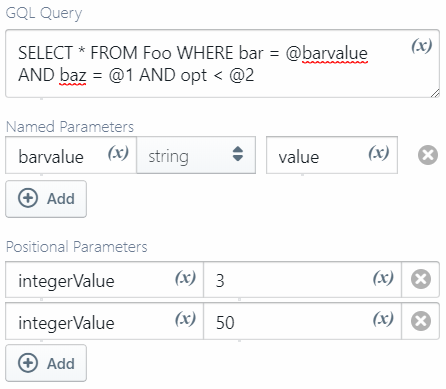
| Field | Required | Supports Variables | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| GQL Query | The GQL query to execute; any parameters must be prefixed with @
|
||
| Named Parameters | A set of key-type-value entries of named parameters in the GQL query. The key must be the parameter name without the @ prefix. |
||
| Positional Parameters | An ordered set of type-value pairs of positional parameters in the GQL query. The type must have a Value suffix: e.g. stringValue, integerValue, geoPointValue, etc. |
On success, response.data will contain a result of the following format,
where batch.entityResults will contain an array of matching entities:
{
"batch": {
"entityResultType": "FULL",
"endCursor": "<base64-encoded>",
"entityResults": [
{
"entity": {
"key": {
"partitionId": {
"projectId": "<project>"
},
"path": [
{
"kind": "<kind>",
"name": "<name>"
}
]
},
"properties": {
"<key-1>": {
"<type-1>": "<value-1>"
},
...
}
},
"cursor": "<cursor>",
"version": "<version-timestamp>"
},
...
]
},
"query": {
"kind": <kind-spec>,
"filter": {
"propertyFilter": <property-spec; property, op and value>
}
}
}
Begin Transaction: projects.beginTransaction
Starts a new transaction for Datastore modification operations. This call does not have any parameters.
On success, response.data will contain a transaction field holding the ID of the started transaction.
This ID should be used when committing or rolling back the transaction later on.
Commit transaction: projects.commit
Commits a previously started transaction, executing a list of data manipulation mutations
| Field | Required | Supports Variables | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transaction ID | ID of the transaction (usually from a previous beginTransaction call) |
||
| DB Operations | A list of mutations to apply along with the commit, each including up to four modification operations |
On success, response.data will contain metadata of the transaction (mutation versions, number of index updates, etc.).
{
"mutationResults": [
{
"version": "<version-timestamp-or-id>"
}
],
"indexUpdates": 8,
"commitVersion": "<commit-timestamp>"
}
Rollback transaction: projects.rollback
Rolls back (cancels) a previously initiated transaction
| Field | Required | Supports Variables | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transaction ID | ID of the transaction to rollback |
On success, response.data will be empty.
Canned operations
In addition to these native operations, Sigma’s Datastore component supports the following
“canned” (convenience) operations for performing a single action (insert, update, etc.) transactionally.
When injected, these are inserted as two service calls;
a beginTransaction followed by a
commit that contains a single operation.
Insert entity
Runs a full transaction with a single entity insert operation
Update entity
Runs a full transaction with a single entity update operation
Upsert entity
Runs a full transaction with a single entity upsert operation
Delete entity
Runs a full transaction with a single entity delete operation